In a current examine printed within the journal Cell, researchers used metagenomics, genomics, and transcriptomics to look at microbiome genomes in over 4,000 metastatic tumor tissues. They analyzed the tumor microbiome and tumor microenvironment (TME), providing organic info and influencing the event of bacteria-focused strategies to complement and enhance most cancers remedies.
Microbial communities play an important function within the human physique, influencing the immune system and anticancer therapies. They’re current in major tumors and work together with the commensal microbiota. The intestine microbiota can modulate immune checkpoint blockers (ICB) and standard chemotherapies. Fecal microbial transplants could enhance medical responsiveness to ICB brokers. Understanding how tumor-resident micro organism form tumor biology, immune infiltration, and remedy responsiveness is important for understanding tumor response to ICB.
 Research: A pan-cancer evaluation of the microbiome in metastatic most cancers
Research: A pan-cancer evaluation of the microbiome in metastatic most cancers
Concerning the examine
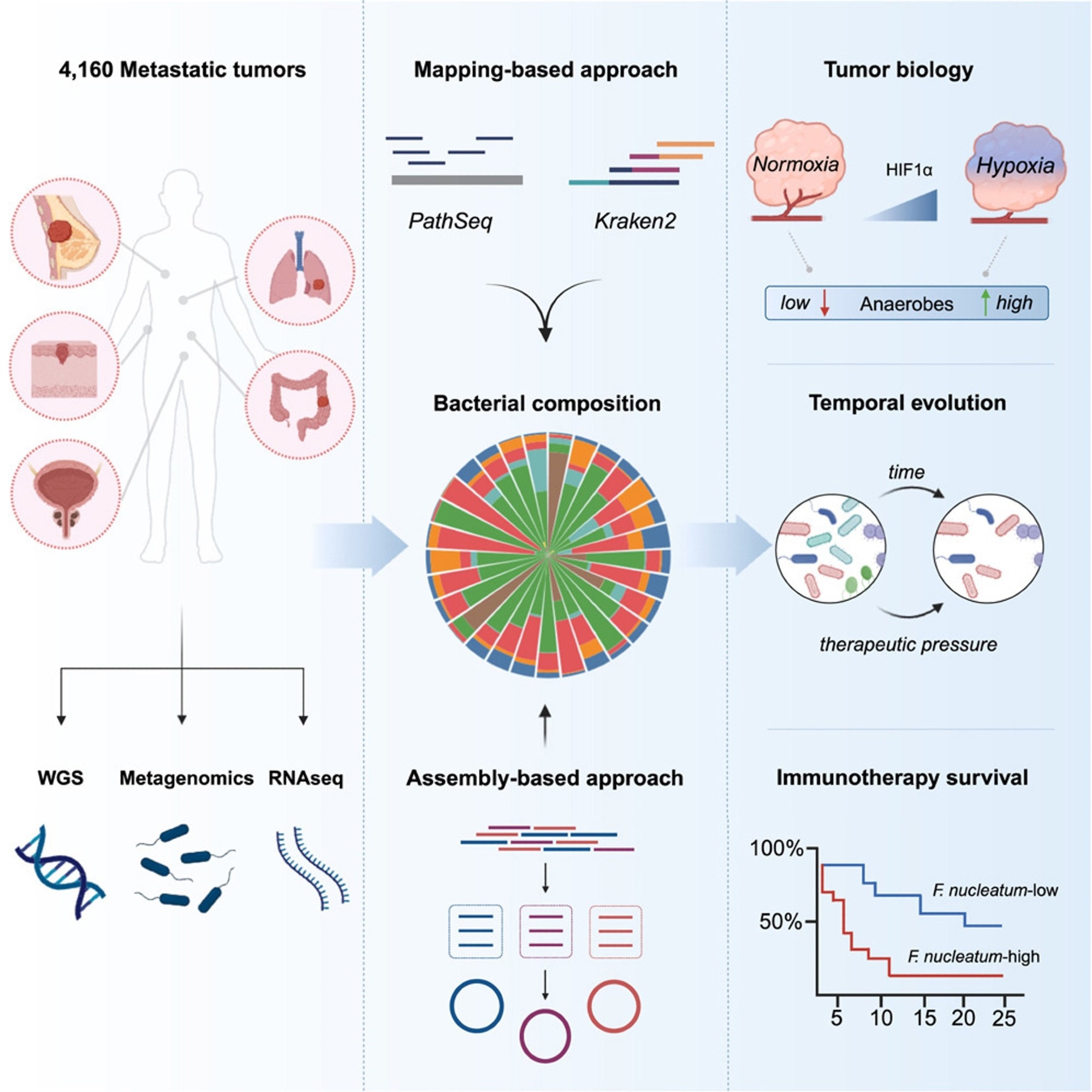
Within the current examine, researchers used bioinformatics to research the microbiota in metastatic malignancies, evaluating 4,160 specimens from numerous most cancers varieties.
The researchers used mapping and assembly-based metagenomics, genomes, transcriptomics, and medical information to develop a pan-cancer repository which may assist advance remedy strategies. They used two distinct computational approaches, PathSeq and Kraken2, to outline tumor-resident microbiome communities on the genus degree and a metagenomic assembly-based strategy on the species degree. The group then formed the metastatic tumor microbiome by figuring out the weather that affect its make-up and evaluating cancer-type-specific microbial communities. They used the attribute hypoxia gene profile to evaluate the diploma of hypoxia in metastatic cancers after which carried out gene set enrichment evaluation (GSEA). In addition they investigated whether or not microbial communities could have an effect on host immunity and the TME.
The researchers investigated the connection between gram-negative micro organism in metastases and Toll-like receptor (TLR) expression and whether or not lipopolysaccharide (LPS), obtained from useless or energetic micro organism, performs a major function in TLR4 signaling in metastases. They moreover examined the connection between bacterial make-up and tumor gene expression and the relationships between explicit micro organism and immune cells.
To additional perceive the affect of metastatic heterogeneity and the sturdiness of tumor-resident microorganisms over time, the group examined 185 pairs of 370 repeated tumor specimens obtained from 173 completely different people. They examined bacterial enrichment modifications earlier than and after tumor remedy with immunotherapy, focused remedy, or hormone remedy. In addition they investigated bacterial depend reductions following immunotherapy in responsive sufferers and whether or not these germs have been extra prevalent in non-responsive people earlier than remedy. Lastly, they examined pre-treatment bacterial communities related to an absence of response to immunosuppressive remedy in an ICB-monotherapy cohort of NSCLC sufferers.
Outcomes
The researchers detected tumor-resident micro organism deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) in a pan-cancer metastasis cohort, and assembling tumor-derived bacterial DNA offered species-level genomic characterization. Bacterial range correlated with mobile and molecular tumor immunity traits. In an NSCLC cohort, excessive ranges of fusobacterium DNA suggest a poor immunotherapy response. Researchers discovered organ-specific microbe tropisms, anaerobic micro organism enrichments in hypoxic tumors, hyperlinks between microbial range and tumor-infiltrating neutrophils, and Fusobacterium’s relationship with resistance to ICB remedy in lung most cancers.
Utilizing mapping-based strategies and screening genera to get rid of technical contamination and seldom-seen genera, the group cataloged 165 microbial genera from 3,526 specimens, with 68% facultative/anaerobic and 49% gram-negative anaerobes. They constructed 514 metagenomic-assembled genomes (MAGs) of medium- to nearly high-quality utilizing tumor-derived microbial sequences. The commonest tumor varieties have been colorectal, breast, prostate, lung, and melanoma, with the lymph node, liver, and lung being the commonest metastatic places for tumor samples.
The amount of bacterial-derived reads expressed as a human-mapped genetic learn proportion diverse by most cancers kind, with increased fractions in renal and uterine malignancies and decrease burdens in tumors originating from the mind and spinal wire. Renal and colorectal metastases have been essentially the most numerous, however head and neck metastatic tumors confirmed extra dominant microbial genera.
Tumor-resident microbial communities have been related to tumor biology, with a powerful correlation between LPS load and TLR4 signaling however not gram-positive lipoteichoic acid (LTA) load. Multivariate Cox proportional-hazards modeling confirmed decrease total survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) charges considerably correlated with steady Fusobacterium abundance, contemplating the genome-wide mutational load. Utilizing the pan-cancer dataset, the researchers categorised all tumors as Fuso-high or Fuso-low based mostly on an higher quartile relative abundance cutoff just like beforehand established standards. Fuso-high tumors confirmed significantly decreased cytotoxic, interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), and main histocompatibility advanced (MHC) class II gene expression profiles.
The examine gives the primary large-scale pan-cancer map of intratumor microbiomes in metastatic malignancies, analyzing range throughout anatomical areas, preliminary tumor kind, and remedy responses, together with immunotherapy. The examine confirmed that the metastatic microbiome partially contains anaerobic micro organism which will get altered throughout remedy. The examine additionally found hyperlinks between intra-tumoral microorganisms and the activation of innate immune sensing pathways, indicating that the tumor microenvironment alters by way of direct identification of bacterial ligands.
