In a current research revealed within the Journal of Experimental Medication, researchers recognized the mobile tropism and transcriptome penalties of extreme acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) by infecting human lung tissue and utilizing single-cell ribonucleic acid sequencing (scRNA-seq) to rebuild the transcriptional program in “an infection pseudotime” for distinct lung cell varieties.
Decrease respiratory infections, comparable to coronavirus illness 2019 (COVID-19), are a number one reason behind loss of life worldwide, producing pneumonia and acute respiratory misery syndrome. Understanding their early phases is troublesome. Researchers used classical histopathological approaches and single-cell multi-omic profiling to deduce early phases in human pathogenesis from lung lavage, biopsy, or post-mortem supplies. These approaches reveal a radical image of COVID-19 pneumonia at unparalleled mobile and molecular decision, implying an infection fashions together with alveolar epithelium, capillaries, macrophages, and myeloid cells.
 Research: Interstitial macrophages are a spotlight of viral takeover and irritation in COVID-19 initiation in human lung. Picture Credit score: Dotted Yeti / Shutterstock
Research: Interstitial macrophages are a spotlight of viral takeover and irritation in COVID-19 initiation in human lung. Picture Credit score: Dotted Yeti / Shutterstock
Concerning the research
Within the current research, researchers developed an experimental COVID-19 mannequin to analyze early molecular processes and pathogenic mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 an infection on the mobile stage in native tissues of the human lung.
The researchers established SARS-CoV-2’s mobile tropism and its distinctive and dynamic impacts on host mobile gene expression in particular forms of lung cells. Distinguished targets had been lung-resident macrophages, of which one SARS-CoV-2 takes over transcriptomes, inducing a focused host interferon (IFN) antiviral program, and several other chemokines and pro-fibrotic and pro-inflammatory and cytokines signaling to numerous structural and immunological cells of the lung.
To find out the early levels of COVID-19 in human lungs, the researchers sliced lung tissue obtained from surgical specimens or organ donor people into thick sections and used them for tissue tradition evaluation. Subsequently, they uncovered the tissues to the SARS-CoV-2 USA-WA1 2020 pressure at 1.0 multiplicity of an infection (MOI) for 2 hours earlier than permitting the SARS-CoV-2 an infection to proceed for 2 to a few days. They carried out a plaque check on tradition supernatants.
The researchers separated the slices and examined them by scRNA-seq to judge host and viral genetic expression through the SARS-CoV-2 an infection. In addition they examined the viral RNA molecules’ junctional construction and processing by analyzing the scRNA-seq dataset with the SICILIAN framework. They used molecular atlas markers to differentiate lung cell varieties in wholesome lung slices and measure viral RNA ranges in contaminated cells.
The group carried out multiplexed single-molecule fluorescence in situ hybridization (smFISH) to verify lung cell tropism findings and present contaminated cells. They used single-cell gene expression patterns to determine mobile targets for inflammatory and pro-fibrotic indicators elicited by the SARS-CoV-2 an infection of a-IMs. They devised a way for purifying macrophage populations from human lungs with a SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein-pseudotyped lentivirus (lenti-S-NLuc-tdT) to analyze lung macrophage entrance routes.
The researchers productively contaminated human lung slices cultivated ex vivo with SARS-CoV-2, with manufacturing rising between 24 and 72 hours of tradition. They heat-inactivated, ultraviolet (UV)-treated, or administered 10.0 µM remdesivir, an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitor used as a COVID-19 therapeutic, to stop viral inventory an infection.
Outcomes
The evaluation confirmed that SARS-CoV-2 preferentially infects lively interstitial macrophages (IMs), which might amass a whole bunch of SARS-CoV-2 RNA molecules, comprising >60% of the cell transcriptome and producing dense viral RNA our bodies. Contaminated alveolar macrophages (AMs) exhibit no extreme reactions, with spike (S) protein-dependent viral entrance into AMs using angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and the cluster of differentiation 169 (CD169) and IM entry by way of CD209.
They discovered canonical sub-genomic junctions between the bizarre sequence reads past their 39 terminal areas, indicating canonical-type SARS-CoV-2 messenger RNA (mRNA) manufacturing within the pulmonary cultures. In addition they discovered a whole bunch of recent subgenomic junctions, exhibiting a variety of non-canonical and canonical sub-genomic SARS-CoV-2 RNAs produced throughout pulmonary an infection.
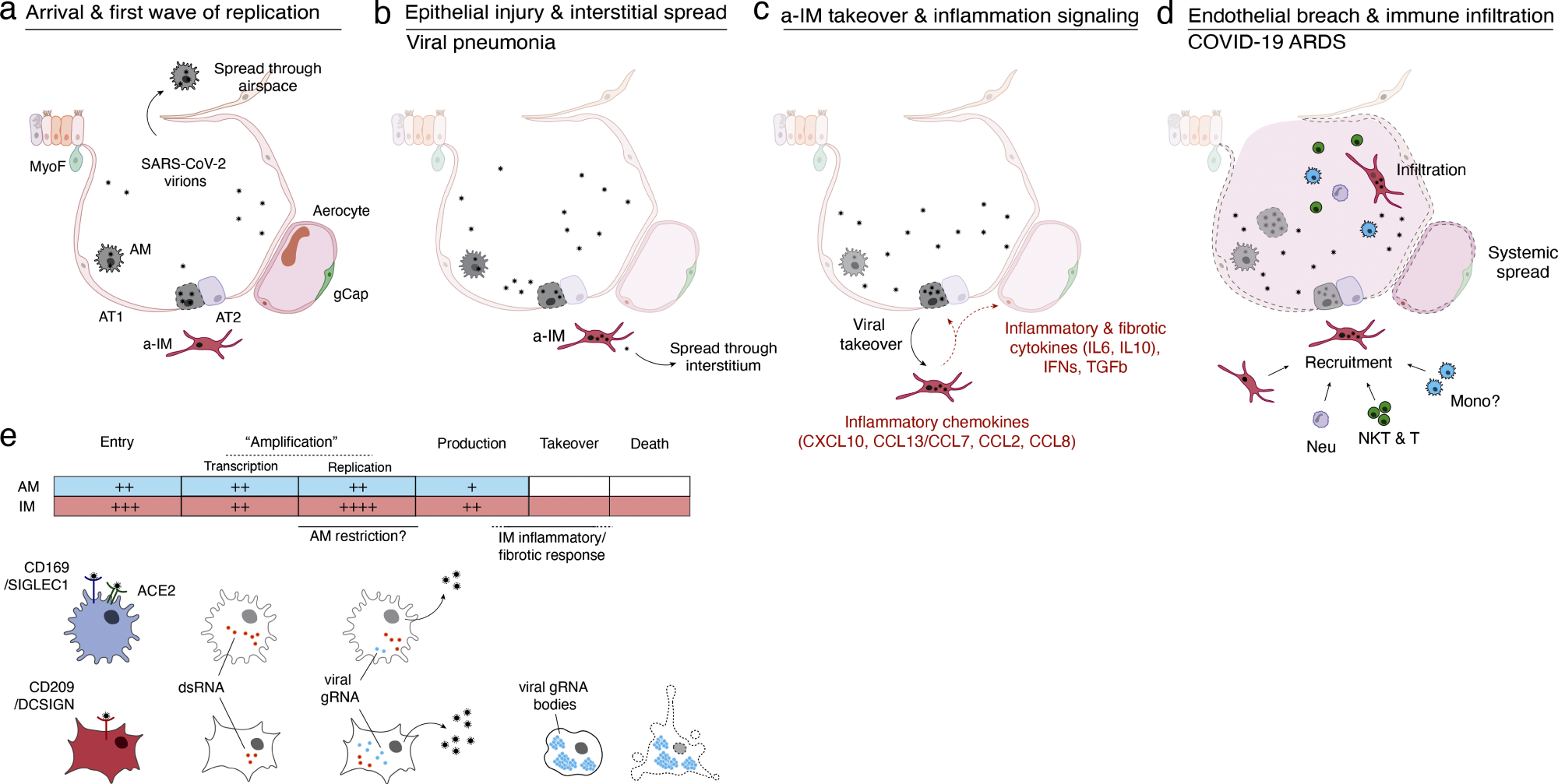 Mannequin of initiation, transition, and pathogenesis of COVID-19 and the viral lifecycle in AMs and IMs. (a–d) Mannequin of COVID-19 initiation within the human lung and transition from viral pneumonia to deadly COVID-19 ARDS. (a) SARS-CoV-2 virion dissemination and arrival within the alveoli. Luminal AM encounter virions shed from the higher respiratory tract that enter the lung. AMs can categorical low to average numbers of viral RNA molecules and may propagate the an infection however “comprise” the viral RNA from taking on the overall transcriptome and present solely a really restricted host cell inflammatory response to viral an infection. (b) Replication and epithelial harm. SARS-CoV-2 virions enter AT2 cells via ACE2, its canonical receptor, and “replicate” to excessive viral RNA ranges, producing infectious virions and initiating viral pneumonia. (c) a-IM takeover and irritation signaling. SARS-CoV-2 virions unfold to the interstitial house via both transepithelial launch of virions by AT2 cells or harm of the epithelial barrier, and enter a-IMs. Contaminated a-IMs can categorical very excessive ranges of viral RNA that dominate (“take over”) the host transcriptome and may propagate the an infection. Viral takeover triggers induction of the chemokines and cytokines proven, forming a spotlight of inflammatory and fibrotic signaling. (d) Endothelial breach and immune infiltration. The a-IM inflammatory cytokine IL6 targets structural cells of the alveolus inflicting epithelial and endothelial breakdown, and the inflammatory cytokines recruit the indicated immune cells from the interstitium or bloodstream, which flood and infiltrate the alveolus inflicting COVID-19 ARDS. Native inflammatory molecules are amplified by circulating immune cells, and reciprocally can unfold via the bloodstream to trigger systemic signs of cytokine storm. (e) Comparability of the SARS-CoV-2 viral lifecycle in AMs and IMs. Though each can produce infectious virions, be aware variations in viral entry receptors (AMs can use ACE2 and CD169/SIGLEC1, whereas IMs use CD209); viral RNA transcription of dsRNA intermediates (higher in AMs); replication of full-length genomic RNA (higher in IMs); viral takeover, formation of RNA our bodies, and induction of a strong host cell inflammatory response (solely in IMs), and cell destruction/loss of life (solely in IMs).
Mannequin of initiation, transition, and pathogenesis of COVID-19 and the viral lifecycle in AMs and IMs. (a–d) Mannequin of COVID-19 initiation within the human lung and transition from viral pneumonia to deadly COVID-19 ARDS. (a) SARS-CoV-2 virion dissemination and arrival within the alveoli. Luminal AM encounter virions shed from the higher respiratory tract that enter the lung. AMs can categorical low to average numbers of viral RNA molecules and may propagate the an infection however “comprise” the viral RNA from taking on the overall transcriptome and present solely a really restricted host cell inflammatory response to viral an infection. (b) Replication and epithelial harm. SARS-CoV-2 virions enter AT2 cells via ACE2, its canonical receptor, and “replicate” to excessive viral RNA ranges, producing infectious virions and initiating viral pneumonia. (c) a-IM takeover and irritation signaling. SARS-CoV-2 virions unfold to the interstitial house via both transepithelial launch of virions by AT2 cells or harm of the epithelial barrier, and enter a-IMs. Contaminated a-IMs can categorical very excessive ranges of viral RNA that dominate (“take over”) the host transcriptome and may propagate the an infection. Viral takeover triggers induction of the chemokines and cytokines proven, forming a spotlight of inflammatory and fibrotic signaling. (d) Endothelial breach and immune infiltration. The a-IM inflammatory cytokine IL6 targets structural cells of the alveolus inflicting epithelial and endothelial breakdown, and the inflammatory cytokines recruit the indicated immune cells from the interstitium or bloodstream, which flood and infiltrate the alveolus inflicting COVID-19 ARDS. Native inflammatory molecules are amplified by circulating immune cells, and reciprocally can unfold via the bloodstream to trigger systemic signs of cytokine storm. (e) Comparability of the SARS-CoV-2 viral lifecycle in AMs and IMs. Though each can produce infectious virions, be aware variations in viral entry receptors (AMs can use ACE2 and CD169/SIGLEC1, whereas IMs use CD209); viral RNA transcription of dsRNA intermediates (higher in AMs); replication of full-length genomic RNA (higher in IMs); viral takeover, formation of RNA our bodies, and induction of a strong host cell inflammatory response (solely in IMs), and cell destruction/loss of life (solely in IMs).
Warmth, UV-C inactivation, or remdesivir remedy prevented the event of canonical and non-canonical connections. The group noticed SARS-CoV-2 takeover of an activated IM subtype in 176,382 cells with high-quality transcriptomes obtained from contaminated lung slices of 4 donor lungs and in 112,359 cells from mock-infected slices (cultured with out viral addition) and 95,389 uncultured management cells (instantly from freshly lower lung slices). A differential gene expression research of a-IMs over an infection pseudotime revealed host gene expression alterations similar to SARS-CoV-2 RNA ranges.
The research discovered that COVID-19 pneumonia an infection and takeover trigger an early antiviral cell response particular to activated interstitial macrophages, leading to a robust immunological and fibrotic signaling middle. Inflammasome activation is rare and solely detectable late in a-IM an infection. Blocking antibodies in opposition to CD169 and CD209 prevented entrance into IMs and AMs. The research additionally highlighted IMs as probably the most weak lung goal, with preliminary emphasis on irritation and fibrosis. Two distinctive molecular lineages of macrophage targets react otherwise to SARS-CoV-2, influencing etiology and coverings.
