This text was initially revealed by Hakai Journal.
There’s an outdated adage about oysters: Throughout months whose names don’t comprise the letter r—Could, June, July, and August—it’s finest to remain away.
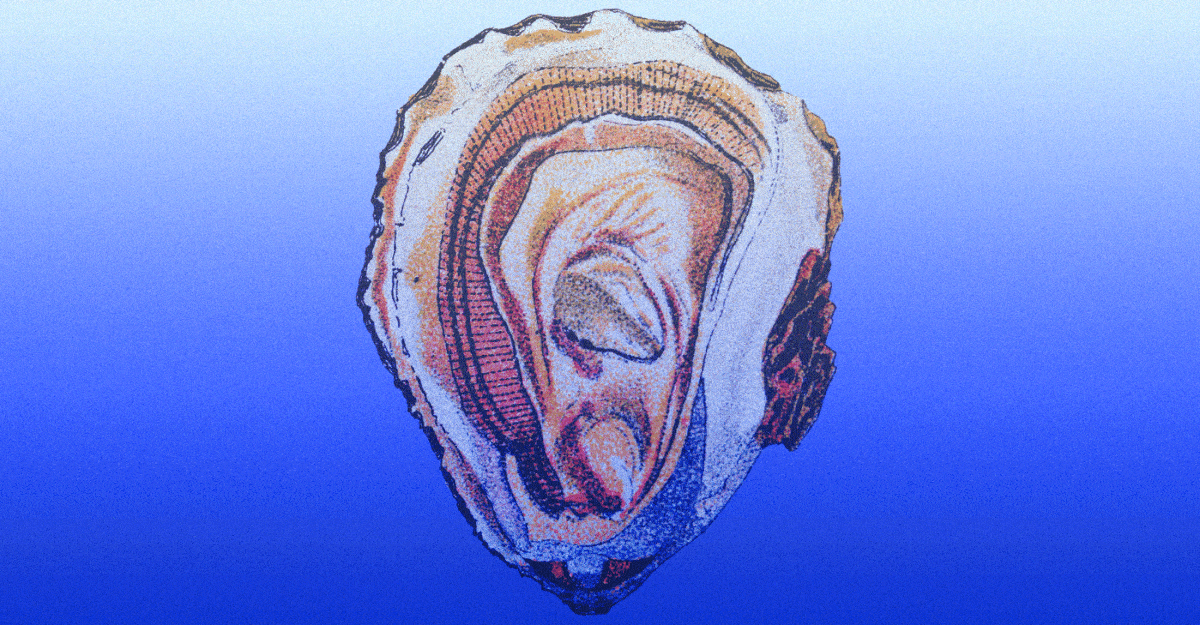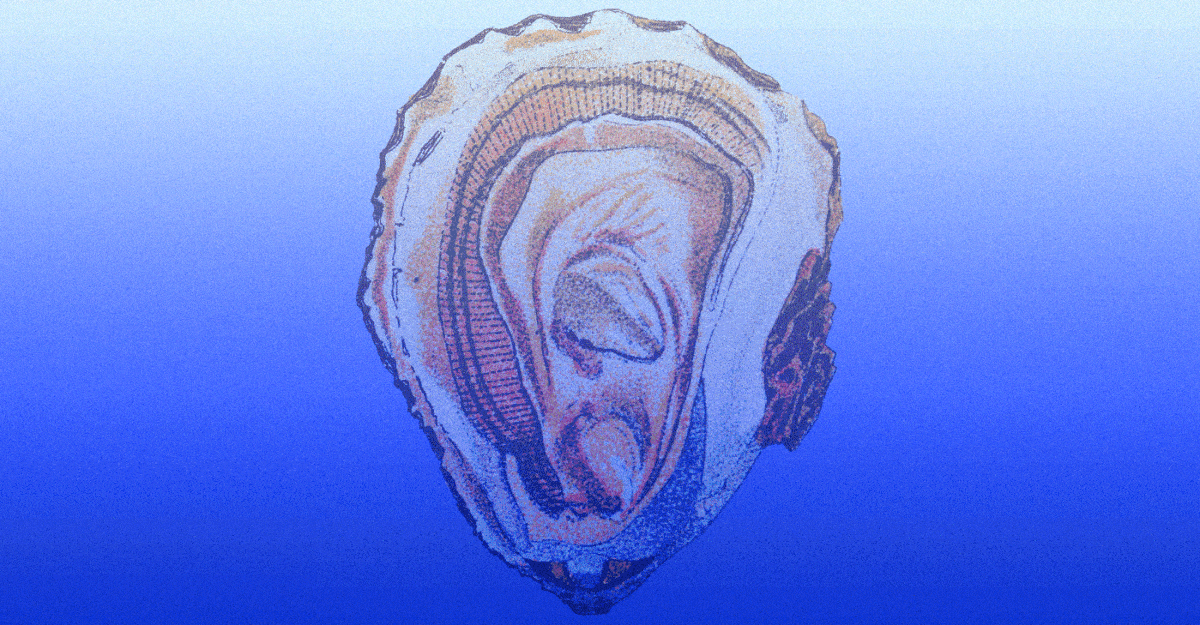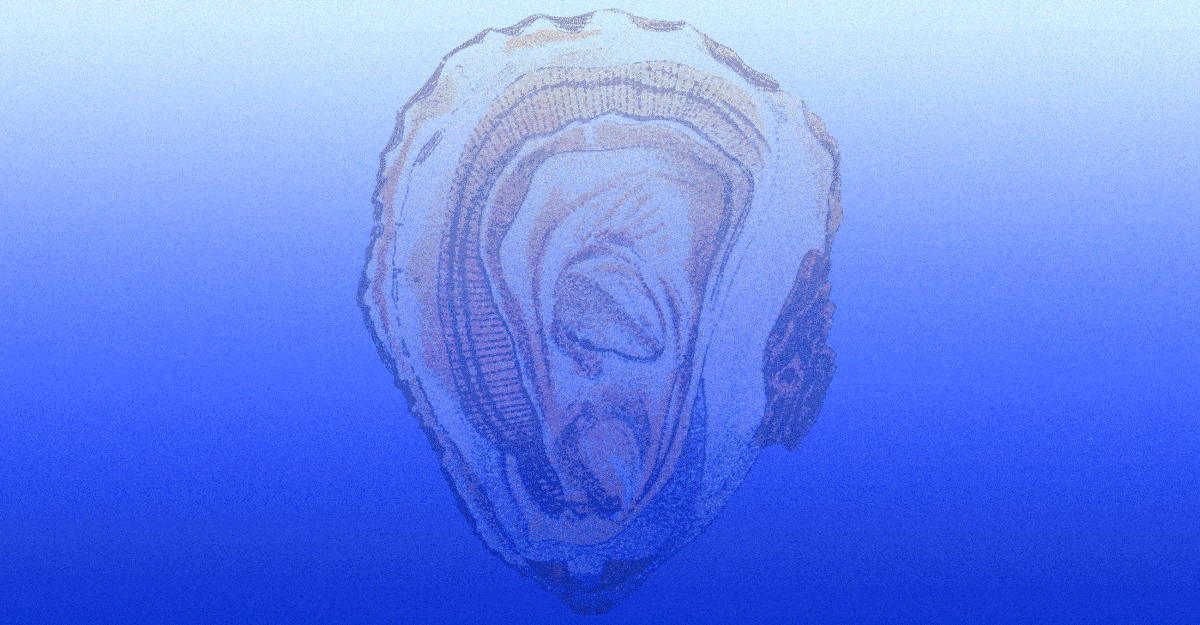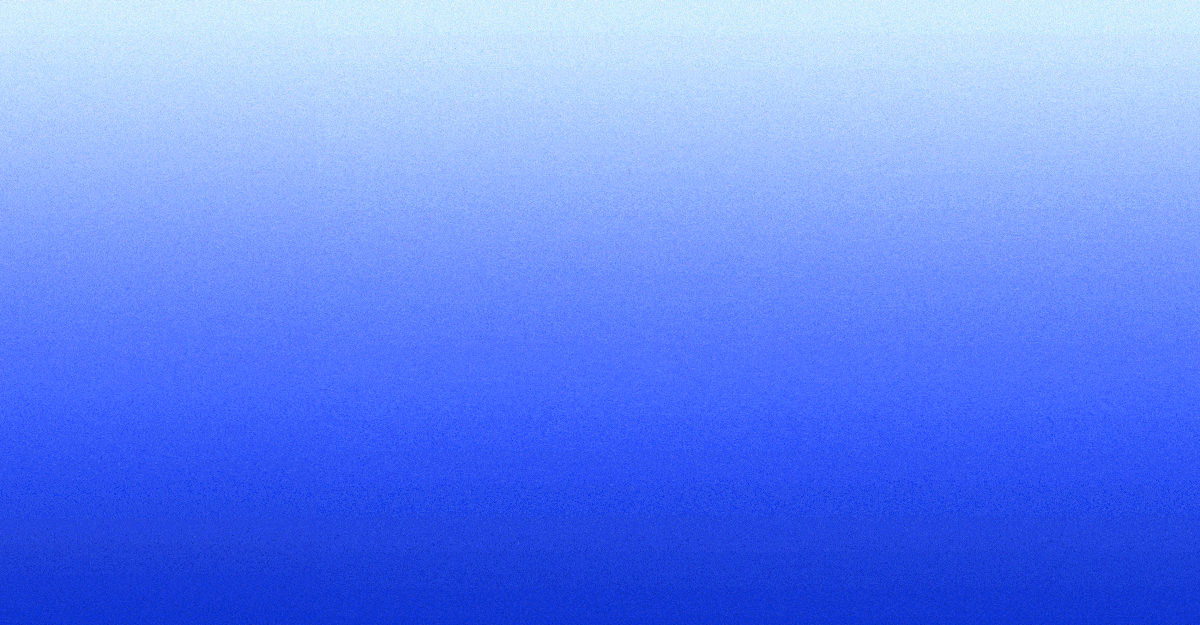
An oyster eaten exterior these months ought to have a satisfying snap, like al dente pasta, says Shina Wysocki, the farm director at Chelsea Farms, in Washington State. That barely agency texture is an indication that you just’re consuming a sexually immature oyster. However summer time oysters—that’s, oysters of their mating season—naturally get flabby, and their gonads swell with gametes. “It’s sperm and eggs,” says Gary Fleener, the senior scientist at Hog Island Oyster Co., in Marshall, California. “It coats your mouth like heavy cream does.” It’s, shall we embrace, an consuming expertise that not everybody finds appetizing.
For many years, nevertheless, oyster customers have been in a position to ignore the standard knowledge about oysters and r months. Rules, refrigeration, and the rise of industrial-scale oyster farming now make it attainable to eat oysters year-round. Much more crucially, within the late Nineteen Seventies, scientists selectively bred a brand new sort of oyster, often known as the triploid oyster, that’s sterile, quicker rising, and fewer “spawny” than its naturally occurring counterparts. The emergence of triploids has untethered oyster consumption from the pure oyster life cycle, and client demand now peaks in the summertime, when folks need chilly beer, chilled wine, and sea treats served on ice.
“Just like how we use selective breeding in watermelon to provide seedless watermelon, you are able to do the identical factor with oysters,” says Matthew George, the coastal-shellfish supervisor for the Washington Division of Fish and Wildlife. In 2016, 50 p.c of all Pacific oysters farmed on the West Coast of america have been triploids. However lately, growers have observed disproportionately increased triploid mortality charges.
A latest examine displaying that triploid oysters could also be extra delicate to excessive warmth than their diploid progenitors has scientists and oyster farmers worrying about the way forward for these delicious shellfish—and questioning whether or not right now’s hotter local weather signifies that our enjoyment of oysters ought to return to a extra seasonally pushed schedule.
Initially, George says, scientists figured that sterile triploid oysters can be extra resilient than their cousins with simply two units of chromosomes. Quite than exerting vitality to provide gonads, he says, the oysters might spend their sources on survival. However over time, oyster farmers have observed that triploid oysters don’t fare as nicely throughout warmth waves—or usually. “Anybody at my farm would inform you that triploids appear to be a bit fussy,” Fleener says.
Within the lab, George and his workforce confirmed triploid oysters’ sensitivity. When uncovered to warmth stress, triploid Pacific oysters die at a charge 2.5 occasions that of the diploids.
Plus, juvenile triploid oysters (identified within the trade as “seed”) are costlier than diploid seed—and lots of farmers have gotten much less prepared to gamble on such poor odds for survival.
Wysocki, of Chelsea Farms, used to purchase triploid seed however isn’t at the moment rising any. “I spent some huge cash on triploid seed to have them die,” she says. Equally, about eight years in the past, Washington-based Taylor Shellfish Farms was planting 70 p.c triploids and 30 p.c diploids. That ratio has now flipped. And in 2022, Washington’s Hama Hama Oyster Firm was planting 24 p.c triploids. That quantity is now all the way down to 18 p.c, says Adam James, the final supervisor of shellfish operations on the firm: “We’ve sort of moved away from buying numerous triploids, as a result of we have been seeing higher mortalities.”
With world temperatures on the rise, triploids are more likely to undergo. What does this imply for an trade during which client demand is at its peak when common diploid oysters are too sexually ripe for many individuals’s palate? Will customers should readapt to oysters’ pure seasonal variability? Or ought to farmers and scientists double down on creating extra resilient triploid oysters?
5 years in the past, Taylor Shellfish Farms began engaged on the latter. The corporate started selectively breeding oysters within the hope of ultimately creating triploid oysters that survive higher within the ocean.
Neil Thompson, an oyster geneticist on the U.S. Division of Agriculture, can be working to selectively breed extra disease-resistant diploid Pacific oysters with the purpose of then breeding triploid oysters which are much less delicate to environmental stressors. The trick is to determine particular heritable traits that correlate with survival after which choose for these as a way to strengthen the oyster’s local weather adaptability.
Within the meantime, West Coast oyster farmers can proceed to satisfy summer time demand by discovering methods to diversify the origins of their oysters, akin to by sourcing the shellfish from colder areas when temperatures rise. After all, transport oysters from afar emits planet-warming carbon dioxide, so oyster growers are additionally exploring different methods, together with suspending their creating oysters in deeper, cooler water to delay spawning.
Then there’s the advertising and marketing angle. “Perhaps we have to discover the language to speak a few creamy oyster with out utilizing the phrase spawny or gonad,” James says.
So far as client habits goes, farmers and restaurant homeowners don’t need to deter anybody from having fun with oysters in the summertime. Quite, they encourage folks to additionally search the shellfish throughout the seasonal peak—when the climate is chilly, the oysters have a snap, and the complicated flavors imbued by the native bays and inlets are worthy of a chef’s kiss.