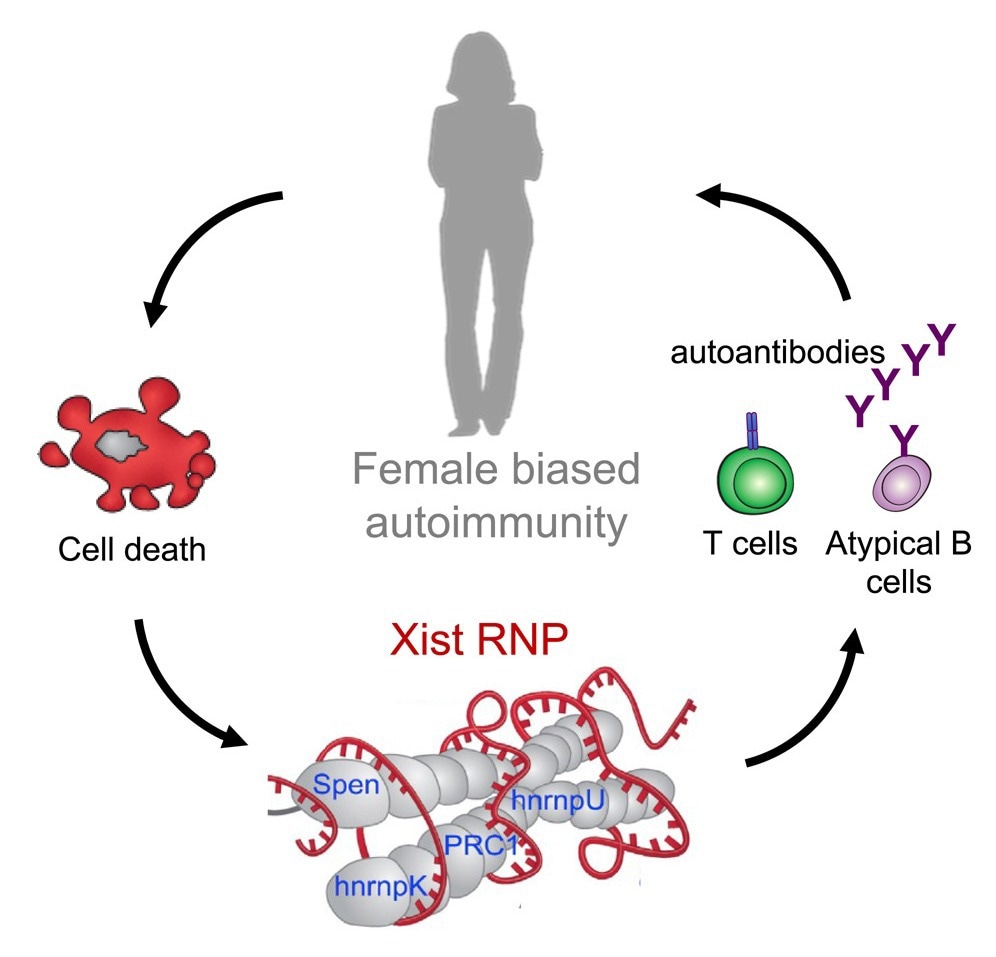
In a latest examine printed within the journal Cell, a staff of scientists predominantly from Stanford College found that sex-biased autoimmunity, the place females are extra affected by autoimmune issues than males, is primarily pushed by the Xist ribonucleoprotein complicated containing varied autoantigenic parts.
 Examine: Xist ribonucleoproteins promote feminine sex-biased autoimmunity. Picture Credit score: Kateryna Kon / Shutterstock
Examine: Xist ribonucleoproteins promote feminine sex-biased autoimmunity. Picture Credit score: Kateryna Kon / Shutterstock
Background
After most cancers and heart problems, autoimmune issues are essentially the most prevalent class of illness, with females having a four-fold greater incidence of autoimmune ailments than males. Sjögren’s illness has a 19 to 1 feminine to male prevalence, whereas the intercourse ratio of systemic lupus erythematosus sufferers is 9:1 for females to males. Moreover, Klinefelter syndrome sufferers who’ve XXY intercourse chromosomes and are phenotypically male with hormonal patterns of a organic male even have the identical danger of autoimmune issues as females.
Whereas the function of hormones has been extensively studied in relation to autoimmune issues, analysis signifies that no matter hormone standing and intercourse, X chromosome dosage appears to be one of many main drivers of autoimmune illness danger. Moreover, research amongst similar twins point out that the penetrance of autoimmune illness may range, suggesting that environmental elements can affect the genetic disposition to autoimmune issues. X-linked genes resembling toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) have been thought to contribute to the event of some autoimmune issues.
In regards to the examine
Within the current examine, the researchers used autoimmune-resistant and autoimmune-prone mouse fashions, C57BL/6J and SJL/J, respectively, to grasp the function of X chromosome dosage compensation in figuring out the disproportionate danger of autoimmune ailments in females.
Since mammalian females have two copies of the X chromosomes as in comparison with mammalian males, who’ve an XY genotype, one of many two X chromosomes in females is epigenetically silenced for dosage compensation in each cell by a mechanism involving a 19-kb pair lengthy non-coding ribonucleic acid (lncRNA) referred to as Xist. Xist will not be expressed in males, and solely the inactive X chromosome transcribes this lncRNA in females.
Research in embryonic stem cells from mice have proven that X chromosome inactivation is established when Xist kinds a ribonucleoprotein complicated with 81 binding proteins which might be distinctive to this complicated. Xist binds on to 10 of those binding proteins by RNA-protein interactions, and to the remaining 71 not directly by protein-protein interactions. A number of of those binding proteins have beforehand been recognized as autoantigens and are thought to activate innate immune system pathways by toll-like receptors.
Right here, the researchers used non-silencing alleles of Xist that have been inducible and launched them into the autosomes of the autoimmune-resistant and autoimmune-prone mice strains. The induction of Xist ribonucleoprotein complicated formation in male mice of a chemically induced systemic lupus erythematosus mouse mannequin allowed this female-specific course of to be noticed in a male background.
RNA sequencing and ATAC-sequencing or assay of transposase-accessible chromatin by sequencing have been used to evaluate modifications in gene expression in splenic CD4+ T cells and potential transcription regulation alterations. Principal part evaluation was additionally used to find out similarities between male mice expressing the induced Xist allele.
Serum samples from handled mice have been additionally assessed for antigens towards scleroderma and systemic lupus erythematosus. Moreover, serum samples obtained from human sufferers of systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, and scleroderma have been examined for reactivity towards proteins from the Xist ribonucleoprotein complicated.
Outcomes
The outcomes reported that the induction of transgenic expression of non-silenced Xist in male mice fashioned Xist ribonucleoprotein complexes and led to the manufacturing of autoantibodies. Male autoimmune-prone mice fashions of pristane-induced systemic lupus erythematosus confirmed multi-organ pathology that was extra extreme than that seen within the wild-type mice. Moreover, the expression of Xist within the male mice had reprogrammed the chromatic states and the B and T cell populations to be extra just like these present in wild-type feminine mice.
The reactivity towards a number of proteins from the Xist ribonucleoprotein complicated was additionally discovered to be vital within the serum samples obtained from human systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, and scleroderma sufferers.
The findings spotlight the potential for utilizing these Xist ribonucleoprotein complex-associated proteins as novel antigens for detecting and monitoring autoimmune ailments. The invention of atypical B cell accumulation as a consequence of Xist ribonucleoprotein complicated expression additionally gives a possible space of analysis for autoimmune dysfunction remedy.
Conclusions
General, the findings indicated that the Xist ribonucleoprotein complicated selectively expressed in females and concerned in X chromosome dosage compensation drives sex-biased autoimmunity. Sufferers with autoimmune circumstances resembling scleroderma and systemic lupus erythematosus have greater reactivity towards proteins from the Xist ribonucleoprotein complicated, highlighting the potential use of those proteins as antigens for screening and early detection of autoimmune issues.
Journal reference:
- Dou, D. R., Zhao, Y., Belk, J. A., Zhao, Y., Casey, Ok. M., Chen, D. C., Li, R., Yu, B., Srinivasan, S., Abe, B. T., Kraft, Ok., Hellström, C., Sjöberg, R., Chang, S., Feng, A., Goldman, D. W., Shah, A. A., Petri, M., Chung, L. S., & Fiorentino, D. F. (2024). Xist ribonucleoproteins promote feminine sex-biased autoimmunity. Cell, 187(3), 733-749.e16, 10.1016/j.cell.2023.12.037, https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(24)00002-3
