In a current analysis letter printed within the journal Nature Growing old, researchers used proteomic sequencing of sufferers’ and controls’ cerebrospinal fluids to analyze the heterogeneity of Alzheimer’s illness. Their findings revealed 5 molecular subtypes that depicted distinct genetic danger components and illness pathologies, together with development charges and survival occasions. These outcomes counsel completely different intervention necessities for every subtype and spotlight the necessity for personalised medication to diagnose and deal with the situation.
 Letter: Cerebrospinal fluid proteomics in sufferers with Alzheimer’s illness reveals 5 molecular subtypes with distinct genetic danger profiles. Picture Credit score: Lightspring / Shutterstock
Letter: Cerebrospinal fluid proteomics in sufferers with Alzheimer’s illness reveals 5 molecular subtypes with distinct genetic danger profiles. Picture Credit score: Lightspring / Shutterstock
Alzheimer’s illness and some great benefits of proteomics
Alzheimer’s illness (AD) is a progressive mind dysfunction predominantly affecting aged people, characterised by the degeneration of neurons accountable for reminiscence and cognition. It’s estimated to have an effect on 5% of people between the ages of 65-74, 13.1% between 75-84, and 33.3% above 84 years, presently affecting 44 million folks, with this quantity rising yearly. AD is acknowledged because the main explanation for dementia worldwide, with no remedy presently recognized and remedy restricted to symptom administration. Whereas a definitive underpinning for the illness is but to be recognized, genetics and environmental publicity are assumed accountable for the situation.
Latest analysis has recognized that AD isn’t a single illness however an umbrella time period for a spectrum of circumstances that fluctuate considerably on the molecular stage. Sadly, these analysis developments invalidate a big physique of earlier literature making an attempt to elucidate the scientific pathophysiology of AD, provided that completely different sufferers could reply considerably otherwise to the identical scientific publicity.
‘Proteomics’ is the examine of the interactions, operate, composition, and buildings of proteins and their mobile actions. It incorporates cutting-edge ‘next-generation’ sequencing strategies akin to mass spectrometry (MS) to determine and characterize 1000’s of protein subunits in biofluids. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is essentially the most accessible of those biofluids referring to neurological circumstances resulting from its fixed contact with the mind and central nervous system (CNS) and its position as a proxy for the mind’s pathophysiological course of.
Concerning the examine
Within the current examine, researchers used a case-control cohort method, utilizing CSF from AD sufferers and age-matched wholesome controls, to disclose the differentially up- and down-regulated proteins in these cohorts through proteomic analyses. The examine pattern group was derived from the Amsterdam Dementia Cohort (ADC), an ongoing examine of all sufferers who’ve sought remedy on the Alzheimer’s Centre in Amsterdam since 2000.
Research inclusion standards comprised identified AD, confirmed based mostly on the presence of an irregular amyloid marker (instances) and age, intercourse, and demographic-matched controls. CSF from each cohorts was collected and subjected to high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) mass spectrometry (MS) – LC-MS/MS. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) have been then used to measure Amyloid-β42, t-tau, p-tau 181, and the amyloid-β42/amyloid-β40 ratio, the primary determinants of AD severity and development stage.
Blood samples from instances and controls have been additional subjected to apolipoprotein E (APOE) genotyping to display screen for single-nucleotide polymorphisms which are recognized to reinforce or suppress AD. T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was used to visualise mind atrophy patterns and consider the variations in AD sufferers’ and controls’ neuroimages. Lastly, standardized neuropsychological take a look at batteries have been administered to check topics throughout preliminary enrollment, with annual follow-up to estimate the speed and diploma of AD development.
Research findings
The current examine included 609 instances and 187 controls. Of the included AD instances, 107 displayed regular cognition, 103 displayed delicate cognitive impairment (MCI), and 209 displayed dementia. LC-MS/MS analyses recognized 3,863 distinctive CSF proteins, of which 1,309 proteins (28,408 peptides) have been frequent to all included contributors and have been used for additional analyses. Of those, cluster analyses revealed 1,058 AD-related proteins. Combining clustering outcomes with sufferers’ scientific traits revealed 5 distinct AD subtypes.
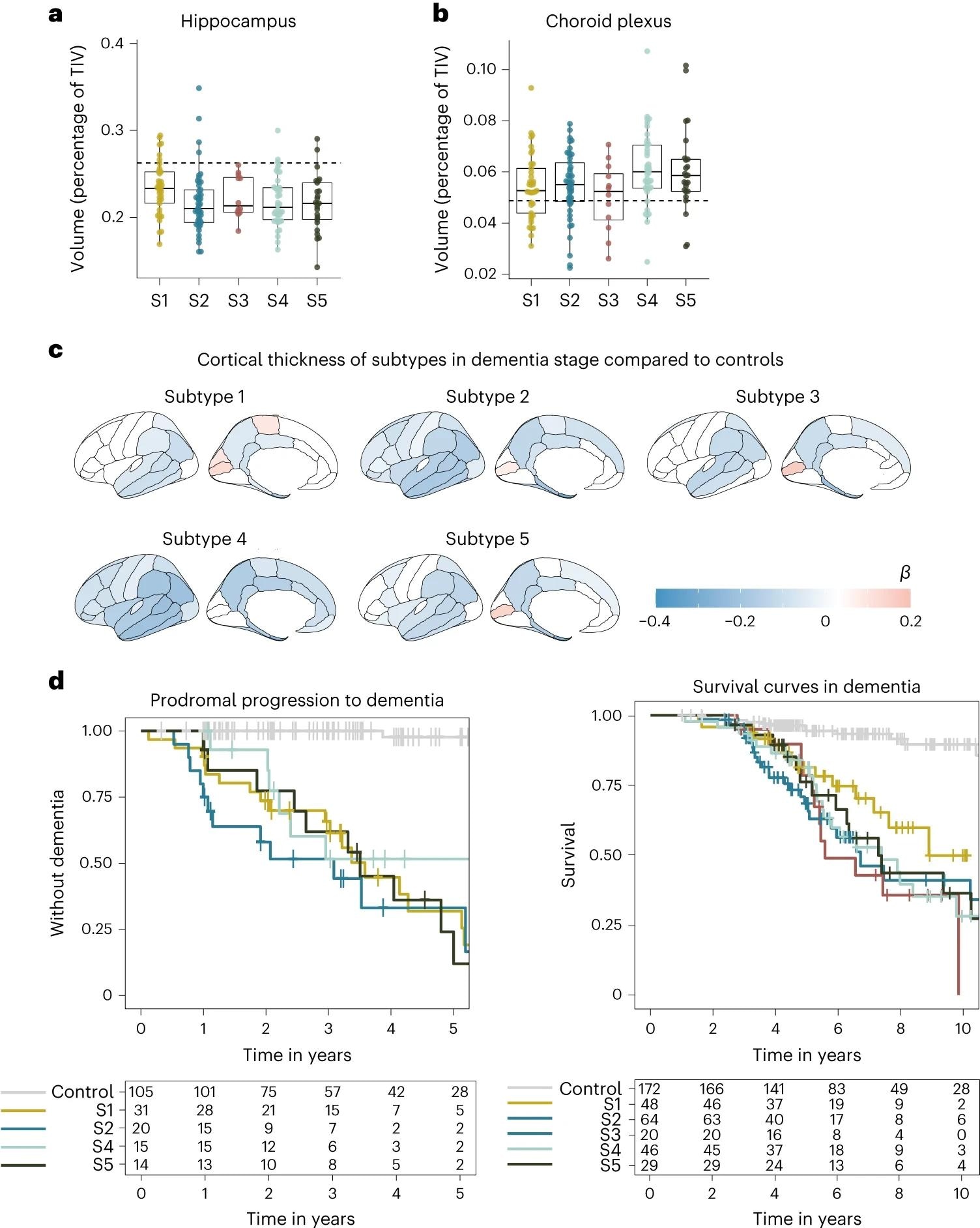 a, Median hippocampal quantity as the proportion of complete intracranial quantity (TIV) in comparison with subtypes within the dementia stage. b, Choroid plexus quantity as the proportion of TIV in comparison with subtypes within the dementia stage. c, Cortical atrophy related to AD subtypes within the dementia stage in comparison with controls (n = 160). β signifies imply cortical thickness in mm, averaged over the correct and left hemispheres and adjusted for age and intercourse. d, Scientific development from MCI to dementia in keeping with subtype (left; excluding subtype 3 resulting from n = 2) and time from dementia to loss of life in keeping with subtypes (proper). All atrophy measures are based mostly on people with dementia solely. a,b, The boxplots depict the median within the heart; the boundaries point out the primary and third quartiles, whereas the whiskers prolong up and all the way down to 1.5 occasions the interquartile vary (restricted to precise noticed information factors), and the factors point out particular person particular person values (subtype 1, n = 37; subtype 2, n = 45; subtype 3, n = 12; subtype 4, n = 40; subtype 5, n = 25).
a, Median hippocampal quantity as the proportion of complete intracranial quantity (TIV) in comparison with subtypes within the dementia stage. b, Choroid plexus quantity as the proportion of TIV in comparison with subtypes within the dementia stage. c, Cortical atrophy related to AD subtypes within the dementia stage in comparison with controls (n = 160). β signifies imply cortical thickness in mm, averaged over the correct and left hemispheres and adjusted for age and intercourse. d, Scientific development from MCI to dementia in keeping with subtype (left; excluding subtype 3 resulting from n = 2) and time from dementia to loss of life in keeping with subtypes (proper). All atrophy measures are based mostly on people with dementia solely. a,b, The boxplots depict the median within the heart; the boundaries point out the primary and third quartiles, whereas the whiskers prolong up and all the way down to 1.5 occasions the interquartile vary (restricted to precise noticed information factors), and the factors point out particular person particular person values (subtype 1, n = 37; subtype 2, n = 45; subtype 3, n = 12; subtype 4, n = 40; subtype 5, n = 25).
Subtype 1 is characterised by neuronal hyperplasticity, subtype 2 by innate immune activation, subtype 3 by RNA dysregulation, subtype 4 by choroid plexus dysfunction, and subtype 5 by blood-brain barrier dysfunction. APOE genotyping corroborated recognized clusters and advised a singular genetic underpinning for every subtype.
“Notably, we discovered that every subtype was related to distinct AD genetic danger components, additional supporting that every CSF AD subtype displays particular underlying molecular mechanisms. The subtypes additionally differed in cortical atrophy patterns and survival occasions, underscoring their scientific relevance.”
Subtypes have been discovered to vary considerably by their scientific pathology, as highlighted by neurophysiological testing – subtype 3 was considerably extra aggressive in its development charge in comparison with the opposite subtypes. Given the diploma of genetic and pathophysiological uniqueness of those subtypes, the necessity for personalised medication turns into obvious.
“…uncomfortable side effects arising from sure remedies can also depend upon subtype. For instance, whereas antibodies could extra simply cross the blood–mind barrier in subtype 5, these people could also be at elevated danger for cerebral bleeding that may happen with antibody remedy.”
Conclusions
The current examine used proteomics to analyze the patient-specific variations in genetic and pathophysiological profiles below the AD umbrella. Research findings reveal greater than 1,000 proteins differentially expressed in AD sufferers, and importantly, that AD includes at the very least 5 distinct subtypes differing of their genetic and scientific underpinnings.
“Given the distinct patterns of molecular processes and AD genetic danger profiles, it’s doubtless that AD subtypes would require particular remedies. For instance, subtype 1 people could profit from TREM2-activating remedies, subtype 2 from innate immune inhibitors, subtype 3 from antisense oligonucleotides that restore RNA processing, subtype 4 from inhibition of monocyte infiltration and subtype 5 from cerebrovascular remedies.”
Journal reference:
- Tijms, B. M., Vromen, E. M., Mjaavatten, O., Holstege, H., Reus, L. M., Wesenhagen, Ok. E., Lorenzini, L., Vermunt, L., Venkatraghavan, V., Tesi, N., Tomassen, J., Den Braber, A., Goossens, J., Vanmechelen, E., Barkhof, F., Pijnenburg, Y. A., M., W., Teunissen, C. E., Berven, F. S., . . . Visser, P. J. (2024). Cerebrospinal fluid proteomics in sufferers with Alzheimer’s illness reveals 5 molecular subtypes with distinct genetic danger profiles. Nature Growing old, 1-15, DOI – https://doi.org/10.1038/s43587-023-00550-7, https://www.nature.com/articles/s43587-023-00550-7
