In a current research revealed within the journal Nature Microbiology, researchers investigated age-related variations in nasal epithelial cell (NEC) responses to extreme acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) an infection throughout pediatric, grownup, and older grownup teams.
 Examine: Age-specific nasal epithelial responses to SARS-CoV-2 an infection. Picture Credit score: Designua / Shutterstock
Examine: Age-specific nasal epithelial responses to SARS-CoV-2 an infection. Picture Credit score: Designua / Shutterstock
Background
Regardless of efficient vaccines, age stays the first threat issue for mortality in coronavirus illness 2019 (COVID-19). SARS-CoV-2 initially infects NECs, which is vital for understanding the development to extreme respiratory points. Additional analysis is required to totally perceive the mechanisms behind age-related variations in response to SARS-CoV-2, which may result in focused therapies and improved outcomes for various age teams.
In regards to the research
Members for the current research had been recruited from 5 main hospital websites in London, United Kingdom (UK), together with the Nice Ormond Road Hospital Nationwide Well being Service (NHS) Basis Belief, the Royal Free London NHS Basis Belief, the College School London Hospitals NHS Basis Belief, and the Whittington Well being NHS Belief, between March 2020 and February 2021. All members consented in writing, and the research was ethically accepted by way of the Residing Airway Biobank, managed by the College School London (UCL) Nice Ormond Road Institute of Baby Well being. People excluded from participation had been present people who smoke, these with lively most cancers or immunodeficiencies, current recipients of blood transfusions, and people with continual respiratory situations akin to bronchial asthma or cystic fibrosis.
Nasal brushings had been collected from wholesome donors throughout three age groups- pediatric (0-11 years), grownup (30-50 years), and older grownup (≥70 years)- who had examined unfavorable for SARS-CoV-2 and confirmed no respiratory signs within the seven weeks previous to sampling. Samples had been collected utilizing cytological brushes and instantly processed to protect cell integrity, following strict pointers.
The NECs had been cultured at an air-liquid interface, contaminated with SARS-CoV-2, and monitored for gene and protein expression adjustments, cell differentiation, and viral replication dynamics.
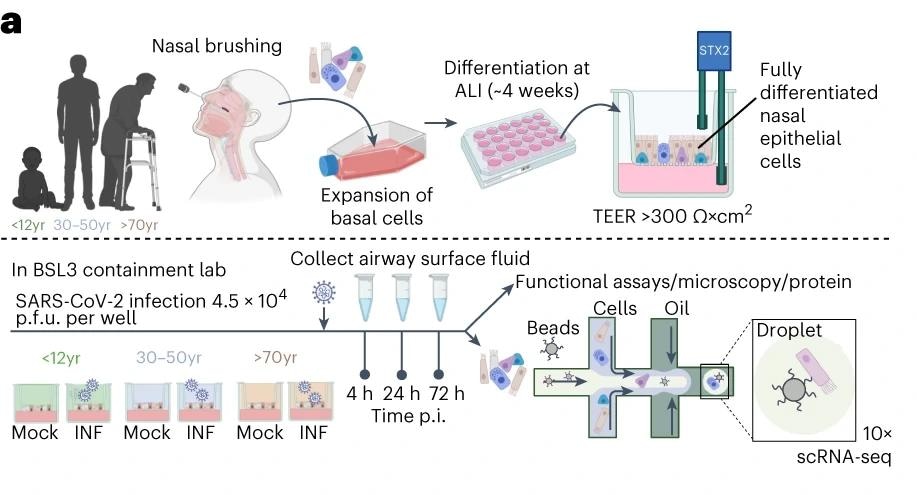
Schematic of methodology and mannequin used to review SARS-CoV-2 an infection of paediatric (P, <12 years), grownup (A, 30–50 years) and older grownup (O, >70 years) nasal epithelial cells.
Examine outcomes
In inspecting the mobile composition of NECs throughout completely different ages, a dataset of 139,598 cells was analyzed utilizing single-cell Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) sequencing, revealing 24 distinct epithelial cell sorts or states. These ranged from basal cells, with subpopulations akin to biking basal and basal|epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) cells, to secretory and ciliated cells, every categorized by distinctive gene expression patterns linked to varied capabilities, together with mucosal protection.
The research additionally famous age-related variations within the distribution of those cell sorts. Adults exhibited a better abundance of basal/progenitor cells in comparison with youngsters, a sample that aligns with findings from earlier nasal epithelial research. Regardless of these variations, ciliary exercise and expression ranges of structural proteins like tubulin confirmed no vital change with age. Nevertheless, NEC cultures from older adults had been noticed to be thicker, suggesting a denser mobile association with out impacting the epithelial barrier’s integrity.
One putting discovering in pediatric cultures was the elevated presence of a particular sort of goblet cell, indicating a shift in cell state not noticed in adults or older people. Regardless of related complete protein ranges of SARS-CoV-2 entry elements amongst all age teams, messenger RNA (mRNA) ranges of those proteins had been distinctly increased in pediatric goblet cells, hinting at a distinct susceptibility to viral an infection throughout ages.
When exploring viral replication dynamics, NEC cultures contaminated with an early-lineage SARS-CoV-2 pressure didn’t present vital variations within the variety of viral reads over time throughout age teams. Nevertheless, the kind of contaminated cells various, with youthful people displaying infections concentrated in fewer cell sorts than adults and older adults. Curiously, older adults confirmed a better viral an infection unfold throughout the tradition, evidenced by a better proportion of cells expressing viral RNA.
The research prolonged to the results of SARS-CoV-2 on cell phenotypes, revealing that an infection led to decreased tradition thickness and compromised epithelial integrity in adults and older adults. There was additionally a famous enhance in basal cell mobilization in older adults, suggesting a heightened response to an infection involving mobile restore mechanisms and presumably contributing to extra extreme illness outcomes. Moreover, older grownup NECs confirmed a better propensity to precise markers associated to tissue harm and fibrosis, which can clarify the extra pronounced bodily and scientific impacts of COVID-19 noticed in older populations.
Conclusions
To summarize, the research analyzed 139,598 NECs throughout completely different ages, revealing 24 distinct cell sorts utilizing single-cell RNA sequencing. It confirmed age-related variations in cell distribution, with adults having extra basal/progenitor cells and older adults displaying thicker NEC cultures. Pediatric cultures had elevated particular goblet cells, indicating variable susceptibilities to SARS-CoV-2. Whereas viral replication was constant throughout ages, older adults skilled a broader an infection unfold. An infection altered cell phenotypes, lowering epithelial integrity in adults and growing tissue harm markers in older adults, underscoring the significance of contemplating age in COVID-19 methods.
