In a latest analysis paper uploaded to the bioRxiv preprint* server, researchers developed and examined novel bispecific antibodies (bsAbs) comprising each the N-terminal area (NTD) and the receptor binding area (RBD) for his or her efficacy towards emergent extreme acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants of concern (VOCs). These antibodies have been synthesized utilizing monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) from convalescent donors who had beforehand obtained monoclonal antibody-based vaccines.
Encouragingly, two developed bsAbs – CoV2 biRN5 and CoV-biRN7 have been discovered to show broad neutralization efficiency towards a spread of Omicron variants, highlighting their potential in changing present COVID-19 intervention modalities, the latter of that are shedding the arms race to SARS-CoV-2 evolution. These NTD-RBD bsAbs could type the idea for a brand new era of anti-COVID-19 vaccines and antibody-based therapeutics towards the illness.
 Research: Bispecific antibodies with broad neutralization efficiency towards SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Picture Credit score: Alpha Tauri 3D Graphics / Shutterstock
Research: Bispecific antibodies with broad neutralization efficiency towards SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Picture Credit score: Alpha Tauri 3D Graphics / Shutterstock

 *Vital discover: bioRxiv publishes preliminary scientific experiences that aren’t peer-reviewed and, subsequently, shouldn’t be thought to be conclusive, information scientific observe/health-related conduct, or handled as established info.
*Vital discover: bioRxiv publishes preliminary scientific experiences that aren’t peer-reviewed and, subsequently, shouldn’t be thought to be conclusive, information scientific observe/health-related conduct, or handled as established info.
Why do we have to reinvent the (COVID-19 therapeutic) wheel?
The coronavirus illness of 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic stays the worst pathogenic outbreak in recorded human historical past, claiming greater than 7 million lives and infecting virtually 800 million people since its discovery in China in late 2019. Whereas government-enforced social distancing measures helped forestall the unfold of the illness through the early days of the pandemic and particularly throughout recurrent prevalence surges, most researchers agree that the one most vital consider finally controlling the illness and stopping additional lack of life, livelihood, and infrastructure was the speedy improvement and government-aided (in some instances mandated) dissemination of anti-COVID-19 vaccines.
Sadly, vaccines are preventive interventions towards subsequent infections, not cures for sufferers already contaminated by the pathogen. Within the latter cohort and for susceptible immunocompromised people, a urgent want for extra scientific interventions to deal with ongoing infections is required. Conventionally, monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have been developed as a protected and efficient anti-COVID-19 remedy. mAbs are proteins produced by a single immune cell cohort that binds to a particular receptor on the goal (herein, the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein), thereby inactivating the pathogen and permitting the physique’s innate immune system to degrade or excrete the virus.
Anti-COVID-19 mAbs are derived from COVID-19 convalescent donors and, given their specificity, symbolize a major enchancment in efficacy over conventional broad-spectrum antivirals, with considerably fewer unintended effects. Sadly, SARS-CoV-2 is a quickly evolving virus – the emergence of novel Omicron variants of concern (VOCs) with modified binding domains resulted in drastic mAb efficacy reductions, thereby leading to a urgent want for the event of novel therapeutic interventions towards the illness.
“We not too long ago recognized NTD-specific nAbs directed to epitopes outdoors the location i antigenic supersite that exhibit potent neutralization and broad binding specificity towards early VOCs. Given the low immune stress on epitopes outdoors the antigenic supersite on the NTD, we hypothesized {that a} non-NTD supersite nAb may show efficient towards the most recent Omicron VOCs when built-in into an NTD-RBD bsAb.”
In regards to the examine
Within the current examine, researchers used nAbs (particularly these focusing on the C1533 non-NTD supersite) derived from convalescent COVID-19 donors to develop a household of novel bispecific antibodies (bsAbs) which they then examined in vitro and in murine fashions towards a bunch of novel Omicron VOCs, notably XBB.1.5, BA.2.86, and EG.5.1. They started by isolating heavy and light-weight chain immunoglobulin G (IgGs) for every antibody and cloning them into an AbVec2.1 expression plasmid. Subsequently, these IgGs have been subcloned and co-transfected into Expi293F cells for Fab assemble expression. Affinity and size-exclusion chromatography have been lastly used to isolate and purify IgGs and Fabs of curiosity.
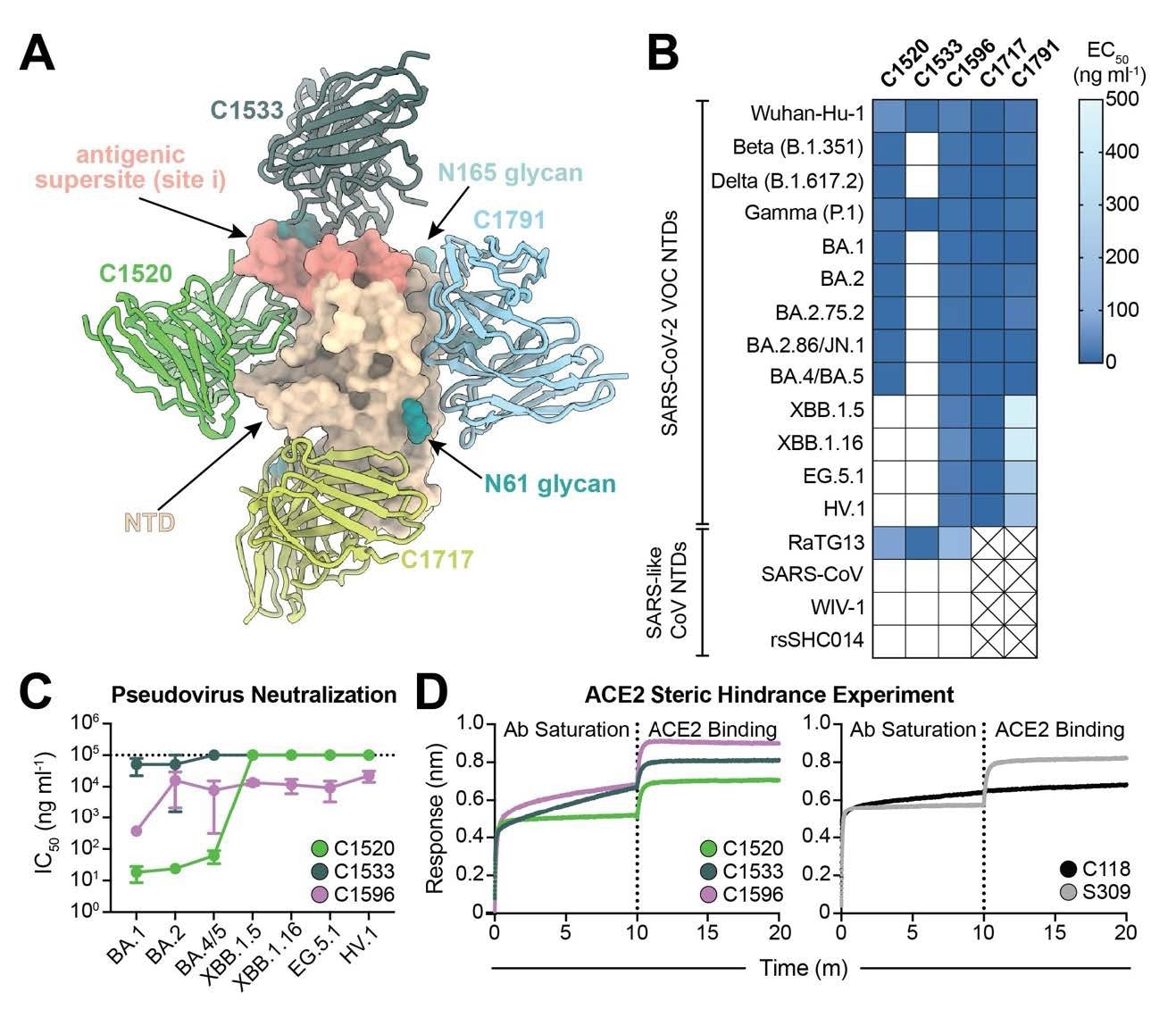
C1596, an NTD-specific mAb, reveals broad binding and neutralizing potential throughout SARS-CoV-2 Omicron VOCs. (A). Superimposition of C1520 (PDB: 7UAQ, inexperienced), C1717 (PDB: 7UAR, lime-yellow), C1791 (blue), and C1533 (darkish slate grey) VH and VL domains onto the SARS-CoV-2 Wuhan-Hu-1 NTD (wheat) for a composite determine. (B) Heatmap of ELISA EC50 values of NTD-specific monoclonal IgG antibodies binding to recombinant NTD protein of SARS-CoV-2 VOCs (high) and SARS-like CoVs (backside). Packing containers shaded white symbolize EC50 values above 500 ng ml-1; bins with an X point out proteins that weren’t examined. Knowledge factors are represented by the geometric imply of not less than three impartial experiments. (C) Graph with IC50 values of NTD-specific IgG antibodies towards the indicated SARS-CoV-2 VOCs. Reported knowledge are represented by the imply of not less than three replicate experiments and the usual error of the imply. (D) BLI affiliation curves for soluble human ACE2 binding to SARS-CoV-2 Wuhan-Hu-1 S 6P trimer after saturation with (left) NTD IgGs and (proper) RBD IgGs. S309 IgG, an RBDspecific antibody (43) that doesn’t compete with ACE2 for binding (43), is used as a management for profitable ACE2 binding following antibody saturation of the trimer; C118 IgG, an RBD-specific antibody (23) that competes with ACE2 for RBD binding (42), is used as a management for competitors with ACE2.
Researchers then developed 9 bsAbs (CoV2-biRN1 to CoV2-biRN9) utilizing a bunch of bsAbs-specific modalities, together with the CrossMab, Xmab, twin variable area immunoglobulin (DVD-Ig) bispecific, and tandem single-chain fragment variable (scFv) bispecific codecs. Every developed bsAbs was then cloned into an AbVec2.1 expression vector and transfected into Expi293F cells for protein expression (4 days at 37˚C). Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) have been used to preliminarily consider the binding efficacy between these Abs and viral antigens. Binding kinetic knowledge between Abs and viral antigens was measured utilizing biolayer interferometry (BLI).
For in vitro evaluations, plasmids obtained above have been transfected into HHEK293T cells for 72 hours, following which generated pseudovirions have been harvested (centrifugation), filtered, and incubated for ~20 hours (37˚C and 5% CO2). For in vivo murine neutralization evaluations, K18-hACE2 transgenic mice have been used (two cohorts – remedy and prophylaxis). Mice have been inoculated with 2 x 104 PFU of SARS-CoV2 XBB.1.5 through intranasal administration. The remedy arm was inoculated with bsAbs 4 hours following XBB.1.5 administration whereas the prophylaxis arm was handled 24 hours earlier than the viral inoculation. Three days following the experiment initiation, mice have been sacrificed, and their left lung was excised for biochemical and microscopic investigations.
Research findings and conclusions
The current examine reveals that the C1596 NTD-specific antibody reveals outstanding cross-reactivity to all examined SARS-CoV-2 VOCs, suggesting that it acknowledges a quaternary epitope comprising the NTD, RBD, and SD1 domains inside a single spike protomer. It was discovered to show a considerably slower dissociation price (okayd) in comparison with monomeric NTD, suggesting the mechanisms unpinning its resilience to viral spike mutations. When integrated within the bispecific format (bsAbs), six of the seven developed bsAbs utilizing C1596 displayed considerably greater VOC neutralization efficacies than their dad or mum mAbs in each in vitro and in vivo evaluations.
“Notably, amongst these constructs, CoV2-biRN5 and CoV2-biRN7 demonstrated sustained neutralization efficacy throughout all VOCs examined. These constructs have been designed with C1596 positioned N-terminal to C952, differing from CoV2-biRN4 and CoV2-biRN6 (C952 on the N-terminus), which exhibited decrease potencies. Collectively, these findings underscore the strategic significance of antibody orientation and the sequential order of binding occasions in designing efficient bispecific therapeutics towards SARSCoV-2.”
In abstract, the current work underscores the advantages of bsAbs in COVID-19 an infection interventions and highlights CoV-biRN5 and CoV-biRN7 as potential blueprints for creating a brand new era of versatile antibodies. The authors suggest preclinical testing on these and equally developed antibodies, paving the best way for his or her eventual scientific translation.
���� New preprint alert from our lab led by the wonderful @adonisrubio99 describing structural investigation and engineering of bispecific antibody constructs resilient to all SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern so far!!! ������❄️�� https://t.co/GPqWWpv3wT
— Christopher Barnes, Ph.D. (@cobarnes27) Might 7, 2024

 *Vital discover: bioRxiv publishes preliminary scientific experiences that aren’t peer-reviewed and, subsequently, shouldn’t be thought to be conclusive, information scientific observe/health-related conduct, or handled as established info.
*Vital discover: bioRxiv publishes preliminary scientific experiences that aren’t peer-reviewed and, subsequently, shouldn’t be thought to be conclusive, information scientific observe/health-related conduct, or handled as established info.
Journal reference:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Rubio, A. A., Baharani, V. A., Dadonaite, B., Parada, M., Abernathy, M. E., Wang, Z., Lee, Y. E., Eso, M., Phung, J., Ramos, I., Chen, T., El Nesr, G., Bloom, J. D., Bieniasz, P. D., Nussenzweig, M. C., & Barnes, C. O. (2024). Bispecific antibodies with broad neutralization efficiency towards SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Chilly Spring Harbor Laboratory, DOI – 10.1101/2024.05.05.592584, https://www.biorxiv.org/content material/10.1101/2024.05.05.592584v1
